Incorruptible Blockchain Insurance - Latest Trends Gaining Ground in America

Updated: September 19th, 2023
In the evolving landscape of the insurance industry, blockchain insurance solutions are reshaping traditional practices. Currently, established industry leaders like IBM Corporation, Microsoft, Oracle, and AWS hold significant market shares. Nevertheless, as blockchain technology for insurance continues to advance and integrates with cloud deployment, emerging players are swiftly gaining ground, expanding their reach in burgeoning markets.
Recent market statistics project a remarkable growth trajectory, with the blockchain insurance market expected to achieve a staggering growth. It is expected to top a CAGR of over 67.4% between 2023-2028, reaching $71 billion - Research and Markets Report.
Insurers are strategically embracing blockchain in the insurance industry to harness the power of the Internet of Things (IoT) for data collection in emerging economies. The implementation of blockchain insurance use cases holds the promise of significantly enhancing operational efficiency. Industry data showcases that blockchain technology can reduce claims processing times by up to 40%, leading to cost savings of 15-20% for insurers. Moreover, blockchain's inherent security ensures the tamper-proof capture of sensory information, establishing a foundation of trust in the industry while expediting claims processing and combating fraud.
Why BlockChain in the Insurance industry will gain more visibility
US Auto Insurer Elephant Insurance revealed a data breach that occurred in March 2022 which exposed the data of its customers. Unauthorized perpetrators accessed the names, driver’s license numbers, and card numbers of not only current and previous customers but also the data through the quoting process of prospective customers. This is why blockchain technology is gaining an impetus in the insurance industry. Blockchain smart contracts make it possible to transfer data through fortified cybersecurity protocols making intermediaries obsolete.
Combined with artificial intelligence and Big Data, blockchain can create a trusted, unfilterable, repository of data. This is why blockchain in insurance could become the future of an industry that has been the target of increasing instances of fraud, human error, and most concerning of all - cyberattacks.
|
The 7 technology trends that are disrupting the insurance sector:
|
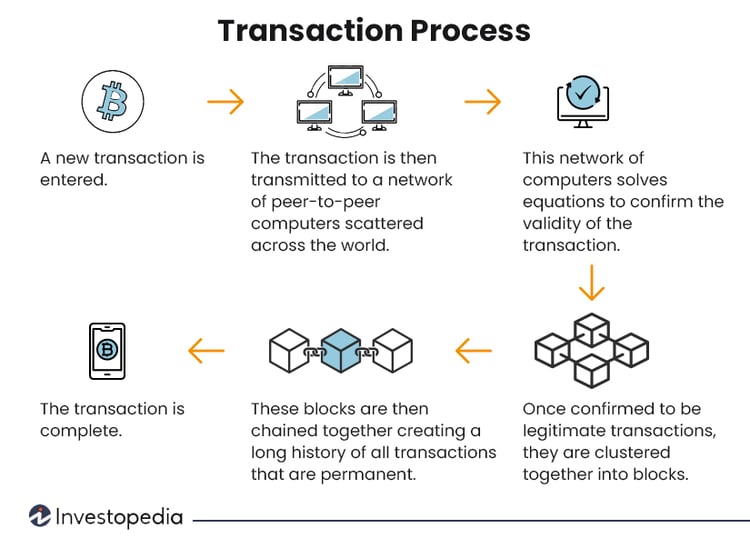
What is a blockchain-trusted ecosystem?
Blockchain stores data but it differs in its structure from a typical database which uses tables for storage. A blockchain collects data in groups called ‘blocks’. Each block has a specific storage capacity. Once filled, it is closed and gets linked to a previously filled block, forming a chain. All new information is compiled into a new block and the chain goes on. In effect, this structure creates an irreversible timeline of data, with each block in the chain getting a specific timestamp when it is filled.
The goal of a blockchain is to allow data to be filled but not overwritten or destroyed. While blockchain can store any kind of information such as legal contracts or even product inventory, its structure makes it most suitable as a ledger for transactions and that is why it is also known as distributed ledger technology or DLT. Distributed, because the data is decentralized and that is where the trusted ecosystem factor comes in. What a blockchain does is hold the same data across several network nodes. If someone tries to alter the records at any one instance, the other nodes would remain unaltered. Immediately the other nodes would cross-reference each other to identify the ‘bad actor’. In short, data cannot be tampered with. To validate any new entry, a majority of the decentralized computing power will have to indicate agreement.
The records in a blockchain are encrypted, only authorized owners can decrypt them using a public-private key pair. This has two advantages, users of blockchain can remain anonymous and still preserve transparency.
Also Read: AI for Insurance - Everything You Need to Know
Blockchain insurance use cases - impact in 4 specific areas
Going by industry statistics, banks in the United States, Japan, and Switzerland are already accepting cryptocurrency transactions. The insurance sector is waking up to its possibilities. The technology is still in its infancy when it comes to insurance carriers, even though many of the big insurance organizations have already started testing blockchain applications. There are 3 areas where blockchain smart contracts are expected to bring the greatest advantage:
1. Writing insurance policies using smart contracts
Insurance policies when written through a smart contract will have software algorithms that will stipulate the rules between the two parties. Smart contracts are programs that are stored in a blockchain that will automatically execute the agreed terms based on predetermined payout scenarios. Since it eliminates any human intervention, the risk of manipulation by any third-party intermediary is almost non-existent.
In case of a fraudulent claim or if the insurance company does not agree to cover terms it had agreed on earlier then the smart contract will immediately dissolve and there is restitution to the harmed party. This automation of tasks is expected to create a greater sense of mutual trust since data is transparent. This could be a solution to a YouGov poll where 43% of Americans said they did not trust their insurance companies.
2. Automating critical steps in the claims process
Smart contracts in the context of blockchain insurance use cases play a pivotal role in automating critical steps within the claims process. For instance, when a policyholder submits a claim to their insurer, a smart contract can execute tasks such as swiftly verifying the customer's coverage validity and seamlessly transmitting this verification to the party responsible for assessing damages liability.
A compelling real-world illustration of blockchain's transformative impact in this domain can be found in the collaborative effort between State Farm and USAA. These companies have harnessed blockchain technology to create a digital ledger, which serves as a comprehensive record of owed amounts. This ledger, in turn, facilitates the simplification of payments by allowing for netting out of obligations and enabling regular consolidated payments. This innovative approach demonstrates how blockchain is revolutionizing insurance processes and fostering efficiency and transparency in claims settlement.
3. Blockchain will bring in advanced automation capabilities
The market size of Property, Casualty and Direct insurance in 2022 is $843.6bn. Health insurance numbers are also staggering with 159 million Americans with employer-based coverage and another 84 million with other coverages. An insurance ecosystem this vast can get bogged down by inefficiencies, impacting both time and money.
A digital ledger system inherent in blockchain technology will automate many of the processes, reduce human error and save billions of hours that go into paperwork. Workflows can send email notifications to users when contracts are about to expire and information from smart contracts can be used to fill in related documents or trigger events. This just skims the surface of the possibilities and as blockchain technology matures more use cases will be revealed.
4. Cybersecurity
Blockchain itself cannot be hacked through blockchain adjacent processes can be hacked. Blockchains are naturally decentralized so there is no central system that can be hacked or manipulated by one authority. All data is also chronologically stamped so there is a record of events.
However, there have been reports of hacking into the Bitcoin universe. The distinction that has to be made here is that in all these instances, the hackers have exploited the vulnerability of the bitcoin bridges. A bridge is software that allows users to send their tokens out of one blockchain network to another cryptocurrency network.
The vulnerability in these bridges can be traced back to some shortcuts in engineering when developing these connecting bridges. The cryptocurrency network, Ronin, announced one of the biggest Bitcoin heists in April 2022. The weak link was because of the limited set of validators that were required to validate a transaction - in the case of Ronin, only 5 out of 9 validators had to be convinced to hand over their key.
Blockchain frauds are almost always targeted at the weakest link - the human operator. As the Ronin hack exposed, once private keys for digital assets are obtained by hackers, they are off to the races. Better regulated safeguarding practices are on the anvil to address this gap.
Hurdles in blockchain acceptance in Insurance
Insurance carriers such as Liberty Mutual, State Farm, and USAA have started testing blockchain applications. They are all partners in the RiskStream Collaborative - a blockchain consortium representing 31 risk management and insurance companies. The collaborative launched Canopy in 2018, the industry’s first custom blockchain architecture that features claims and policy blockchains that are the foundation of most insurance use cases.
While blockchain technology is known more for the hype surrounding cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin, its truly transformative force might lie in industries like insurance where there are numerous intermediaries coordinating with each other. There is a catch though since insurance is a regulated sector, there might be significant legal hurdles before initiatives like the RiskStream collaboration can find greater acceptance - we are getting there.
Topics: Digital Transformation