Cybersecurity for Insurance Companies: Is Risk Minimized in the Cloud?

The traditional cat and mouse game between insurance carriers and hackers have now advanced to a new level. A report published by Ernest & Young puts 2020 into the spotlight as the year which saw an unprecedented rise in the number of cybersecurity attacks on businesses. Industries that suffered ransomware attacks in 2020 paid out $370 million in cryptocurrency - a whopping 336% more than in 2019. One of the main reasons probably is because Covid-19 forced organizations into ad-hoc measures that bypassed cybersecurity protocols.
The proliferation of advanced internet tools has also meant that virtually anyone can become a cyber hacker. In fact, ransomware-as-a-service is available on the dark web for those looking for it. Putting up as many barriers as possible between sensitive data and cyber thieves might seem like a Bond movie probably but yes there are ways to make it as difficult as possible to get through the protective shield.
The emergence of cloud hosting in insurance
For a long time, many insurers preferred their on-premise insurance systems to cloud hosting as they believed they had tighter control over the former, allowing them to regulate security measures better. However, this has changed. The most obvious push for shifting to the cloud was the urgent need to create a mobile remote workforce but also because digital transformation needs the cloud.
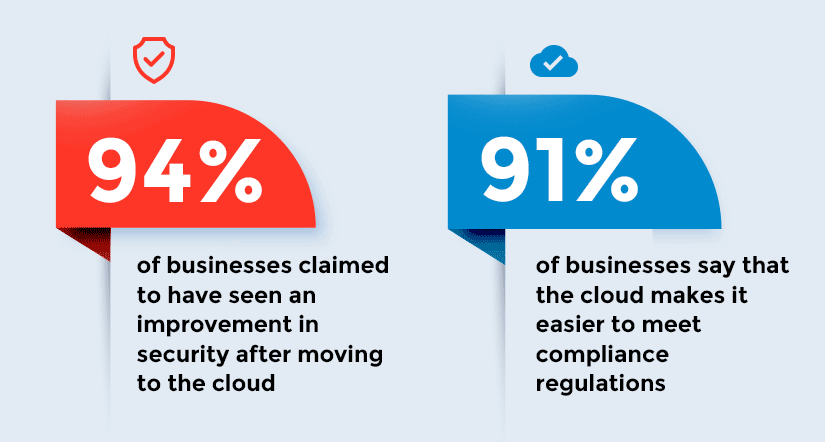
The long-term advantage of the cloud though is the greater protection it offers carriers from cyber threats. There are five crucial ways in which the cloud can improve cybersecurity for insurance companies.
-
Security is in-built into the solution
Cloud security is an integral part of the software, rather than just being an add-on feature. The leading cloud hosting providers often differentiate themselves by the sophistication of their cybersecurity systems. Using a cloud provider also means that companies can be assured that their security is constantly being monitored and upgraded. The advanced level of cyber threats companies now face means that simply conducting routine audits might not offer adequate progression.
Microsoft Azure invests over $1 billion annually in cybersecurity research and development for Azure cloud service, alone.
Cloud providers often have a dedicated cloud security team that is constantly identifying threats and closing loopholes. This proactive approach and sophisticated cloud security measures minimize the risk of cyber hackers compromising data. Vulnerabilities are resolved before hackers can take advantage of them, which improves cybersecurity for insurance companies. In the Solarigate attack recently, an intern used a naive "solarwinds123" password that hackers used to inject their code into on-premise software that was then distributed during an update into the systems of Homeland security and other departments. It also reached 8,000 customers worldwide, through Microsoft's services. The hack was exposed only when it hit the cloud services. The hack was successful only because on-premise identity systems are easier to compromise.
Also read: Brain vs Bot: Does RPA in Insurance Need Intelligent Automation?
-
Data is protected at all stages
Insurance carriers are seeing a greater demand from customers for self-service and insurance mobile apps. While these features can undoubtedly improve customer experience, allowing more users into the system comes with a certain level of risk. With insurance mobile apps, for example, data needs to be transferred from the main storage center (where it’s at rest) to the user’s app (where it’s in transit). Protecting data at both stages is crucial. Data in transit is particularly vulnerable to leaks as hackers can tap into the wireless channels it uses during transmission.
Cloud security measures can protect data at rest and in transit through cloud data security features like encryption and multi-factor authentication. Encryption ensures that cyber hackers cannot decode data even if they do get access to it, while multi-factor authentication ensures that only users authorized to access the data can view it.
-
Users are provided with role-based access
Role-based access is another way of ensuring that users only access what they are allowed to. Within a company, this means that a junior employee within a certain department will not have the same view as a senior employee in the same department. Lower designations will have limited authorization to make changes or perform other activities using the customer data. Departments will also not be able to view data from other departments.
Crucially, very few people, if any, on cloud-based insurance systems will have universal access to data. This is very important to mitigate both malicious use of data as well as hacking a company’s data through an employee’s ID. Role-based access also comes in useful when an employee’s access needs to be revoked fast. In the 24 hours it generally takes to successfully revoke access, an employee’s visibility into the data remains fairly limited, so they are unable to misuse or export it.
-
Security lapses can be traced
In an on-premise setup, tracing the origins of a data leak can be a time-consuming process as there is rarely a traceable footprint left behind. In on-premise setups, tracking down the origins of the leak and the extent of information that was leaked could be a very long-drawn-out process. With increased time to resolve the security lapse, a greater amount of information would be leaked and the fines insurance companies face are potentially higher. Public clouds, however, ensure every action taken leaves a digital footprint. In the event data is compromised, stakeholders will get alerted immediately and can access details of exactly how and where the leak took place. This can help companies rectify issues much faster and minimize damage.
Related read: Authorization and Authentication Process: 5 Ways to Fix Security Gaps
-
The cost of cybersecurity on the cloud is lower
Tight post-pandemic budgets have meant that CIOs cannot allocate as many resources to cybersecurity as they might have wanted to. Companies are looking to urgently invest in technologies that enable them to work remotely and cater to changing customer expectations. But without an equal emphasis on improving the security infrastructure, companies could be making themselves more vulnerable to cyberthreats.
The cloud, however, allows insurance carriers to free up their resources as cloud security is an in-built function. Public cloud providers take full responsibility for maintaining and improving security systems in the cloud. Because of this, companies do not need a dedicated team and budget for cybersecurity.
The cloud is emerging as the single most efficient technological infrastructure for insurance carriers. Cloud data security can help lower the cost of IT maintenance, strengthen cybersecurity, and prevent malicious attacks that could do irreversible damage to a carrier’s reputation.
Topics: A.I. in Insurance






.jpg)